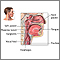
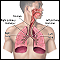
Acute upper airway obstruction
An acute upper airway obstruction is a blockage of the upper airway, which can be in the trachea, voice box (laryngeal), or throat (pharyngeal) areas.
Causes
Causes of acute upper airway obstruction include:
- Allergic reactions in which the trachea or throat swell closed, including allergic reactions to a bee sting, peanuts, antibiotics (penicillin), and blood pressure medications (ACE inhibitors)
- Chemical burns and reactions
- Croup
- Epiglottitis (infection of the structure separating the trachea from the esophagus)
- Fire or burns from breathing in smoke
- Foreign bodies -- such as peanuts and other breathed-in foods, pieces of a balloon, buttons, coins, and small toys
- Viral or bacteria infections
- Peritonsillar abscess
- Retropharyngeal abscess
- Throat cancer
- Tracheomalacia
- Trauma
- Vocal cord problems
Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the cause, but some symptoms are common to all types of airway blockage. They include:
- Agitation or fidgeting
- Bluish color to the skin (cyanosis)
- Changes in consciousness
- Choking
- Confusion
- Difficulty breathing
- Gasping for air
- Panic
- Unconsciousness
- Wheezing, crowing, whistling, or other unusual breathing noises indicating breathing difficulty
Exams and Tests
Physical examination may show:
- Decreased breath sounds in the lungs
- Rapid, shallow, or slowed breathing
Tests are usually not necessary, but may include:
- Bronchoscopy
- Laryngoscopy
- X-rays
Treatment
If the person has a complete obstruction and is unable to speak or breathe, the Heimlich maneuver may be lifesaving.
Treatment depends on the cause of the blockage.
- Objects stuck in the airway may be removed with a laryngoscope or bronchoscope.
- A tube may be inserted into the airway (endotracheal tube or nasotracheal tube).
- Sometimes an opening is made directly into the airway (tracheostomy or cricothyrotomy).
Outlook (Prognosis)
Prompt treatment is often successful. However, the condition is dangerous and may be fatal, even if treated.
Possible Complications
Inability to relieve the obstruction can cause:
- Brain damage
- Breathing failure
- Death
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Airway obstruction is an emergency. It is a good idea to learn how to clear an airway of a foreign body by using a method such as the Heimlich maneuver.
Diseases in which airway obstruction develops over a period of hours will allow time to get to a hospital. If an acute airway obstruction occurs, call 911 or your local emergency number for medical help. Do what you can to maintain breathing until medical help arrives.
Prevention
Prevention depends on the cause of the upper airway obstruction.
The following methods may help prevent an obstruction:
- Eat slowly and chew food completely.
- Don't drink too much alcohol before or while eating.
- Keep small objects away from young children.
- Make sure dentures fit properly
Alternative Names
Airway obstruction - acute upper
References
Manno M. Pediatric respiratory emergencies: Upper airway obstruction and infections. In: Marx J, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 7th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Mosby Elsevier; 2009: chap 166.
Thomas SH, Brown DFM. Foreign bodies. In: Marx J, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 7th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Mosby Elsevier; 2009: chap 57.
Update Date: 4/16/2012
Reviewed by: Jacob L. Heller, MD, MHA, Emergency Medicine, Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, Washington, Clinic. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
Topics
Images
Read More
Notice: The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.