Puberty and adolescence
Puberty is the time in which a child's sexual and physical characteristics mature. It occurs due to hormone changes.
Adolescence is the period between puberty and adulthood.
Information
The exact age a child enters puberty depends on a number of different things, such as genes, nutrition, and gender. During puberty, endocrine glands produce hormones that cause body changes and the development of secondary sex characteristics.
- In girls, the ovaries begin to increase production of estrogen and other female hormones.
- In boys, the testicles increase production of testosterone.
The adrenal glands produce hormones that cause increased armpit sweating, body odor, acne, and armpit and pubic hair. This process is called adrenarche. The child will often need an underarm deodorant or antiperspirant during this time.
PUBERTY IN GIRLS
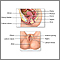
Breast development is the main sign that a girl is entering puberty. The first menstrual period (menarche) usually follows within about 2 years.
Before the first menstrual period, a girl will normally have:
- An increase in height
- An increase in hip size
- Clear or whitish vaginal secretions
- Pubic, armpit, and leg hair growth
Menstrual cycles occur over about 1 month (28 to 32 days). At first, the menstrual periods may be irregular. A girl may go 2 months between periods, or may have two periods in 1 month. Over time, periods become more regular. Keeping track of when the period occurs and how long it lasts can help predict when the next menstrual period will occur.
After menstruation starts, the ovaries begin to produce and release eggs, which have been stored in the ovaries since birth. About every month after menstruation starts, an ovary releases an egg, called an ovum. The egg travels down a Fallopian tube, which connects the ovary to the womb.
When the egg reaches the womb, the lining of the womb becomes thick with blood and fluid. This happens so that if the egg is fertilized, it can grow and develop in the lining to produce a baby. (It is important to remember that fertility comes before emotional maturity, and pregnancy can occur before an adolescent is prepared for parenthood.)
If the egg does not meet with sperm from a male and is not fertilized, it dissolves. The thickened lining falls off and forms menstrual blood flow, which passes out of the body through the vagina. In between the menstrual periods, there may be a clear or whitish vaginal discharge. This is normal.
During or just before each period, the girl may feel moody or emotional, and her body may feel puffy or swollen (bloated). Premenstrual syndrome ( PMS) may begin to develop, especially as the girl gets older.
In girls, puberty is usually finished by age 17. Any increases in height after this age are uncommon. Although a girl has reached full physical maturity at this time, her educational and emotional maturity continue to grow.
PUBERTY IN BOYS
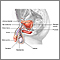
The first sign of puberty in boys is enlargement of both testicles. Afterward, boys will normally experience:
- Faster growth, especially height
- Hair growth under the arms, on the face, and in the pubic area
- Increased shoulder width
- Growth of the penis, scrotum (with reddening and folding of the skin), and testes
- Nighttime ejaculations (nocturnal emissions or "wet dreams")
- Voice changes
The testes constantly produce sperm. Some sperm can be stored in a structure called the epididymis. Sometimes the stored sperm are released as part of the normal process to make room for new sperm. This can occur automatically during sleep (nocturnal emissions) or following masturbation or sexual intercourse. Nocturnal emissions are a normal part of puberty.
ADOLESCENCE
Adolescence is the time between the beginning of sexual maturation (puberty) and adulthood. It is a time of psychological maturation, which a person becomes "adult-like" in behavior.
Adolescence is considered to be the period between ages 13 and 19. The adolescent experiences not only physical growth and change, but also emotional, psychological, social, and mental change and growth.
See also:
- Adolescent depression
- Adolescent pregnancy
- Childhood stress
- Death among children and adolescents
- Suicide
Alternative Names
Maturation - sexual; Adolescence; Reproductive development; Sexual maturation; Menarche; Adrenarche
References
Marcell AV. Adolescence. In: Kliegman RM, Behrman RE, Jenson HB, Stanton BF, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 18th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders Elsevier; 2007:chap 12.
Updated: 4/2/2012
Reviewed by: Jennifer K. Mannheim, ARNP, Medical Staff, Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Health, Seattle Children’s Hospital. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
Notice: The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.