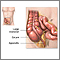
Point tenderness - abdomen
Abdominal point tenderness is the pain you feel when pressure is placed over a certain part of the belly area (abdomen).
Considerations
The abdomen is an area of the body a doctor can easily examine by touch. The doctor can feel growths and organs in the belly area and find where you feel pain.
Abdominal tenderness can range from mild to severe. "Rebound" tenderness occurs when the tissue that lines the abdominal cavity (the peritoneum) is irritated, inflamed, or infected.
See also: Peritonitis
Causes
- Abdominal abscess
- Appendicitis
- Certain types of hernias
- Meckel's diverticulum
- Ovarian torsion (twisted Fallopian tube)
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Any person with point tenderness should call the emergency number (911) or go to an emergency room to be examined right away by a health care provider.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam, which includes gently pushing on areas of your abdomen. Persons with peritonitis will often tense the abdominal muscles when the doctor touches the area. This is called "guarding."
The doctor will note any point tenderness. This is a general term that means you have tenderness in a certain area.
For example, if you have appendicitis, you will likely have point tenderness when a certain part of your belly area is touched. This area is called McBurney's point.
The health care provider will also ask questions about your symptoms and medical history:
- When did the symptoms start?
- Is this the first time you have had such discomfort?
- If not, when does the discomfort tend to occur?
- What other symptoms do you have? For example, do you have:
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Fainting
- Fever
- Vomiting
The following tests may be done:
- Abdominal x-ray
- Abdominal CT scan (occasionally)
- Blood work, such as a complete blood count
In some cases, immediate surgery will be needed. This may involve an exploratory laparotomy or an emergency appendectomy.
Alternative Names
Abdominal tenderness
References
Bengiamin RN, Budhram GR, King KE, Wightman JM. Abdominal pain. In: Marx JA, Hockberger Rs, Walls RM, et al, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 7th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Mosby Elsevier;2009:chap 21.
Postier RG, Squires RA. Acute abdomen. In: Townsend CM, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 18th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders Elsevier; 2008:chap 45.
Updated: 4/28/2012
Reviewed by: Linda Vorvick, MD, Medical Director, MEDEX Northwest Division of Physician Assistant Studies, University of Washington School of Medicine. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
Notice: The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.