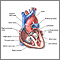
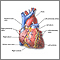
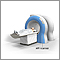
Heart MRI
Heart magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a imaging method that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the heart. It does not use radiation (x-rays).
Single MRI images are called slices. The images can be stored on a computer or printed on film. One exam produces dozens or sometimes hundreds of images.
The test may be done as part of a chest MRI.
How the Test is Performed
You may be asked to wear a hospital gown or clothing without metal fasteners (such as sweatpants and a t-shirt). Certain types of metal can cause blurry images.
You will lie on a narrow table, which slides into into a large tunnel-like tube.
Some exams require a special dye (contrast). The dye is usually given before the test through a vein (IV) in your hand or forearm. The dye helps the radiologist see certain areas more clearly.
During the MRI, the person who operates the machine will watch you from another room. The test most often lasts 30-60 minutes, but may take longer.
How to Prepare for the Test
You may be asked not to eat or drink anything for 4 - 6 hours before the scan.
Tell your doctor if you are afraid of close spaces (have claustrophobia). You may be given a medicine to help you feel sleepy and less anxious, or your doctor may suggest an "open" MRI, in which the machine is not as close to the body.
Before the test, tell your health care provider if you have:
- Brain aneurysm clips
- Certain types of artificial heart valves
- Heart defibrillator or pacemaker
- Inner ear (cochlear) implants
- Kidney disease or dialysis (you may not be able to receive contrast)
- Recently placed artificial joints
- Certain types of vascular stents
- Worked with sheet metal in the past (you may need tests to check for metal pieces in your eyes)
Because the MRI contains strong magnets, metal objects are not allowed into the room with the MRI scanner:
- Pens, pocketknives, and eyeglasses may fly across the room.
- Items such as jewelry, watches, credit cards, and hearing aids can be damaged.
- Pins, hairpins, metal zippers, and similar metallic items can distort the images.
- Removable dental work should be taken out just before the scan.
How the Test Will Feel
A heart MRI exam causes no pain. Some people may become anxious when inside the scanner. If you have difficulty lying still or are very anxious, you may be given a mild sedative. Excessive movement can blur MRI images and cause errors.
The table may be hard or cold, but you can request a blanket or pillow. The machine produces loud thumping and humming noises when turned on. Ear plugs are usually given to help reduce the noise.
An intercom in the scanner allows you to speak to the person operating the exam at any time. Some MRI scanners have televisions and special headphones that you can use to help the time pass.
There is no recovery time, unless sedation was necessary. (You will need someone to drive you home if sedation was given.) After an MRI scan, you can resume your normal diet, activity, and medications, unless otherwise instructed by your doctor.
Why the Test is Performed
MRI provides detailed pictures of the heart and blood vessels from many views. Often, it is used when more information is needed after you have had an echocardiogram or heart CT scan.
Heart MRI may be used to diagnose:
- Heart muscle damage after a heart attack
- Birth defects of the heart
- Heart tumors and growths
- Other reasons for weakening of the heart muscle
- Symptoms of heart failure
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may be due to:
- Heart valve disorders
- Fluid in the sac-like covering around the heart (pericardial effusion)
- Tumor of the blood vessels or around the heart
- Atrial myxoma
- Congenital heart disease (heart problems that you are born with)
- Damage or death to the heart muscle, seen after a heart attack
- Weakening of the heart muscle, can be caused by sarcoidosis or amyloidosis
Risks
There is no radiation involved in MRI. The magnetic fields and radio waves used during the same have not been shown to cause any significant side effects.
Allergic reactions to the dye used during the exam are rare. The most common type of contrast (dye) used is gadolinium. It is very safe. The person operating the machine will monitor your heart rate and breathing as needed. Rare complications can occur in patients with severe kidney problems.
People have been harmed in MRI machines when they did not remove metal objects from their clothes or when metal objects were left in the room by others.
MRI is usually not recommended for traumatic injuries, because traction and life-support equipment cannot safely enter the scanner area, and scans can take a long time.
Considerations
MRI is more accurate than CT scan or other tests for certain conditions, but less accurate for others. MRIs can be costly, take a long time to perform, and are sensitive to movement. Persons with claustrophobia or who are anxious may have difficulty lying still for the scans.
Alternative Names
Magnetic resonance imaging - cardiac; Magnetic resonance imaging - heart; Nuclear magnetic resonance - cardiac; NMR - cardiac; MRI of the heart
References
Kwong RY. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging. In: Bonow RO, Mann DL, Zipes DP, Libby P, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 9th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders Elsevier; 2011:chap 18.
Update Date: 4/22/2012
Reviewed by: David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc., and Michael A. Chen, MD, PhD, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Harborview Medical Center, University of Washington Medical School, Seattle, Washington.
Notice: The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.