Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a test sometimes done during pregnancy that looks for birth defects and genetic problems in the developing baby.
How the Test is Performed
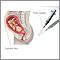
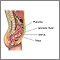
Amniocentesis removes a small amount of fluid from the sac that surrounds the baby in the womb (uterus). It is usually done in a doctor's office or medical center. You do not need to stay in the hospital.
You will probably have a pregnancy ultrasound first. This helps your health care provider find out exactly where the baby is in your womb.
Numbing medicine is then rubbed onto part of the your belly. Sometimes, the medicine is given through a shot in the skin on the belly area.
The health care provider inserts a long, thin needle through your belly and into the womb. A small amount of fluid is removed from the sac surrounding the baby.
How to Prepare for the Test
Your bladder must be full for the ultrasound.
Before the test, blood may be taken to determine your blood type and Rh factor. You may get an shot of medicine called Rhogam if you are Rh negative.
.
How the Test Will Feel
If you get a shot of numbing medicine, you may feel a sharp, stinging sensation for a few seconds.
Some women feel a sharp pain for a few seconds when the needle enters the sac surrounding the baby.
Some women feel pressure in the lower belly area when the fluid is removed. After the procedure, you may have some minor cramping.
Why the Test is Performed
Amniocentesis can be used to diagnose many different gene and chromosome problems in the baby, including:
- Anencephaly
- Down syndrome
- Rare, metabolic disorders that are passed down through families
It can also help:
- Determine how well the baby's lungs are developed
- Detect spina bifida and other neural tube defects
- Detect Rh incompatibility
- Diagnose an infection in the baby
Normal Results
A normal result means:
- No genetic or chromosome problems were seen in your baby
- Bilirubin and alpha fetoprotein levels appear normal
Note: Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your doctor about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An abnormal result may mean your baby has a gene or chromosome problem, or other health condition. Talk to your doctor about the meaning of your specific test results.
DNA testing is available for many of the diseases that may be detected during amniocentesis. Ask your obstetrician or geneticist if you have a question about a specific disease.
Risks
Risks are minimal, but may include:
- Infection or injury to the baby
- Miscarriage
- Leaking of amniotic fluid
- Vaginal bleeding
Considerations
There may be alternatives to the amniocentesis. Discuss these other tests with your health care provider.
Alternative Names
Culture - amniotic fluid; Culture - amniotic cells
References
Simpson JL, Otaño L. Prenatal genetic diagnosis. In: Gabbe SG, Niebyl JR, Simpson JL, eds. Obstetrics:Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 5th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone; 2007:chap 7.
Druzin ML, Smith JF Jr, Gabbe SG, Reed KL. Antepartum fetal evaluation. In: Gabbe SG, Niebyl JR, Simpson JL, eds. Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 5th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone; 2007:chap 11.
Cunningham FG, Leveno KJ, Bloom SL, et al. Prenatal Diagnosis and Fetal Therapy. In: Cunningham FG, Leveno KL, Bloom SL, et al, eds. Williams Obstetrics. 23rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2010:chap 13.
Updated: 4/13/2012
Reviewed by: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Medical Director, MEDEX Northwest Division of Physician Assistant Studies, University of Washington, School of Medicine; Susan Storck, MD, FACOG, Chief, Eastside Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Group Health Cooperative of Puget Sound, Bellevue, Washington; Clinical Teaching Faculty, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Washington School of Medicine. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
Notice: The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.