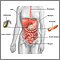
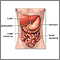
Ischemic colitis
Ischemic colitis is a sudden swelling (inflammation) of part of the large intestine (colon) that occurs when there is a temporary loss of, or reduction in, blood flow to the colon.
Causes
Ischemic colitis mainly affects people over 50. Many of them have a history of peripheral vascular disease.
Other risk factors include:
- Atrial fibrillation
- Blockage of the large bowel
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Congestive heart failure
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Low blood pressure
- Past aortic surgery in which damage occurred to the artery that supplies the colon
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Use of medications that cause constipation
Symptoms
- Abdominal pain
- Blood in the stool (may be bright red or maroon)
- Diarrhea
- Fever
- Vomiting
Exams and Tests
- Colonoscopy or flexible sigmoidoscopy
- Computerized tomography (CT scan)
Treatment
Treatment for mild ischemic colitis often involves:
- Antibiotics
- Liquid diet at first
- Fluids through a vein (by IV)
- Pain medications
Severe ischemic colitis that leads to gangrene is treated with:
- Antibiotics
- Replacement of blood volume
- Surgery to remove the affected bowel area
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most cases of ischemic colitis are mild and will improve on their own. They do not need surgical treatment.
The death rate is high when gangrene occurs because there is not enough blood supply.
Possible Complications
- Gangrene of the bowel
- Hole in the intestine (perforation)
- Inflammation of the lining of the abdomen (peritonitis)
- Sepsis
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if you develop symptoms of ischemic colitis.
Prevention
Being aware of your risk may allow early diagnosis and treatment. Absolute prevention may not be possible.
Alternative Names
Colonic ischemia
References
Hauser SC. Vascular diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. In: Goldman L, Ausiello D. Cecil Medicine. 23rd ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders Elsevier; 2007:chap 146.
Update Date: 1/20/2012
Reviewed by: David C. Dugdale, III, MD, Professor of Mediicne, Division of General Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine; and George F. Longstreth, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Kaiser Permanente Medical Care Program, San Diego, California. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
Notice: The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.