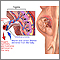
Placental insufficiency
Placental insufficiency is a complication of pregnancy in which the placenta cannot bring enough oxygen and nutrients to a baby growing in the womb. The placenta is the organ that develops during pregnancy to feed a developing baby.
See also: Intrauterine growth restriction
Causes
Certain medical conditions and habits in the mother can lead to placenta insufficiency. These include:
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Medical conditions that increase the mother's chances of blood clots
- Smoking
Certain medications can also increase the risk of placenta insufficiency.
In some cases, the placenta may be abnormally shaped or it may not grow big enough, especially if you are carrying twins or more. Placental insufficiency may also occur if the placenta does not attach correctly to the surface of the womb, or if it breaks away from this surface or bleeds.
Symptoms
A woman with placenta insufficiency usually does not have any symptoms.
Exams and Tests
A pregnant woman should receive proper prenatal care. The health care provider will measure the size of your growing womb (uterus) at each visit, starting about halfway through your pregnancy.
Tests that may be done include:
- Pregnancy ultrasound to measure the growth of the baby (may be done more often than in a normal pregnancy)
- Monitoring of the baby’s heart rate (nonstress test)
You may be asked to keep a daily record of how often the baby moves or kicks.
Treatment
Treating any underlying medical conditions, such as high blood pressure or diabetes, is important, and helps to improve the baby's growth.
Your doctor may tell you rest in bed for some or all of the remainder of the pregnancy.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Problems with the placenta can affect the developing baby's growth. The baby cannot grow and develop normally in the womb if it does not get enough oxygen and nutrients.
In some cases, placenta insufficiency leads to an abnormally low weight in the baby, a condition called intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR). This increases the chances of complications during pregnancy and delivery. For more information, see: IUGR
Possible Complications
Pregnant women with placental insufficiency and IUGR have an increased risk for stillbirth.
Prevention
Getting prenatal care early in pregnancy will help make sure that the mother is as healthy as possible during the pregnancy.
Smoking, alcohol, and other illicit drugs can interfere with the baby's growth. Avoiding these substances may help prevent placental insufficiency and other pregnancy complications.
Alternative Names
Placental dysfunction
References
Baschat AA, Galan HL, Ross MG, Gabbe SG. Intrauterine growth restriction. In: Gabbe SG, Niebyl JR, Simpson JL. Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 5th ed. New York, NY: Churchill Livingstone; 2007:chap.29.
Grivell RM, Wong L, Bhatia V. Regimens of fetal surveillance for impaired fetal growth. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;(1):CD007113.
Update Date: 4/5/2012
Reviewed by: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Medical Director, MEDEX Northwest Division of Physician Assistant Studies, University of Washington, School of Medicine; Susan Storck, MD, FACOG, Chief, Eastside Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Group Health Cooperative of Puget Sound, Redmond, Washington; Clinical Teaching Faculty, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Washington School of Medicine. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
Topics
Images
Read More
Notice: The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.