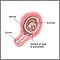
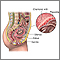
Chorionic villus sampling
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) is the removal of a small piece of placenta tissue (chorionic villi) from the uterus during early pregnancy to screen the baby for genetic defects.
How the Test is Performed
CVS can be done through the cervix (transcervical) or through the abdomen (transabdominal). The techniques are equally safe when done by a provider with experience, although miscarriage rates are slightly higher when done through the cervix. The health care provider will use ultrasound to pick the safest approach and as a guide during sampling.
An abdominal ultrasound is performed to determine the position of the uterus, the size of the gestational sac, and the position of the placenta within the uterus. Your vulva, vagina, cervix, and abdomen are cleaned with an antiseptic.
The transcervical procedure is performed by inserting a thin plastic tube through the vagina and cervix to reach the placenta. The provider uses ultrasound images to help guide the tube into the appropriate area and then removes a small sample of chorionic villus tissue.
The transabdominal procedure is performed by inserting a needle through the abdomen and uterus and into the placenta. Ultrasound is used to help guide the needle, and a small amount of tissue is drawn into the syringe.
The sample is placed in a dish and evaluated in a laboratory.
How to Prepare for the Test
Your health care provider will explain the procedure, its risks, and alternative procedures such as amniocentesis. Genetic counseling is recommended prior to the procedure. This will allow you to make an unhurried, informed decision regarding options for prenatal diagnosis.
You will be asked to sign a consent form before this procedure, and you may be asked to wear a hospital gown.
The morning of the procedure you may be asked to drink fluids and refrain from urinating to fill your bladder, which allows adequate visualization so the sample may be taken.
Tell your health care provider if you are allergic to iodine or shellfish, or if you have any other allergies.
How the Test Will Feel
The ultrasound doesn't hurt. A clear, water-based conducting gel is applied to the skin to help with the transmission of the sound waves. A handheld probe called a transducer is then moved over the area. In addition, your health care provider may apply pressure on your abdomen to find the position of your uterus.
The antiseptic cleansing solution will feel cold at first and may irritate your skin if not washed off after the procedure.
Some women say the vaginal approach feels like a Pap smear with some discomfort and a feeling of pressure. There may be a small amount of vaginal bleeding following the procedure.
An obstetrician can perform this procedure in about 5 minutes, after the preparation.
Why the Test is Performed
The test is a way of detecting genetic disorders. The sample is used to study the DNA , chromosomes, and certain signs (called chemical markers) of disease in the developing baby. It can be done sooner than amniocentesis, about 10 to 12 weeks after your last menstrual period. Test results take about 2 weeks.
Chorionic villus sampling does not detect neural tube defects. If neural tube defects or Rh incompatibility are a concern, an amniocentesis will be performed.
This test can usually not diagnose congenital defects, which are problems in the way the baby's body forms.
Normal Results
A normal result means there are no signs of any genetic defects. However the test could miss some genetic defects.
Note: Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your doctor about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An abnormal result may be a sign of more than 200 disorders, including:
- Down syndrome
- Hemoglobinopathies
- Tay-Sachs disease
Risks
The risks of CVS are only slightly higher than those of an amniocentesis.
Possible complications include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Miscarriage
- Rh incompatibility in the mother
- Rupture of membranes
Signs of complications include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Excessive vaginal discharge
- Fever
Report any signs of complications to your health care provider.
CVS was previously thought to cause limb problems in the developing baby. When CVS is performed after 9 weeks gestational age, this risk appears to be very low (6 per 10,000), and is no more frequent than in pregnancies without this testing.
Considerations
If your blood is Rh negative, you may receive RhoGAM to prevent Rh incompatibility.
You will receive a follow-up ultrasound 2 to 4 days after the procedure to make sure the pregnancy is proceeding normally.
References
Simpson JL, Otano L. Prenatal genetic diagnosis. In: Gabbe SG, Niebyl JR, Simpson JL. Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 5th ed. New York, NY: Churchill Livingstone; 2007:chap. 7.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). Invasive prenatal testing for aneuploidy. Washington (DC): American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG); 2007 Dec. 9 p.
Update Date: 4/5/2012
Reviewed by: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Medical Director, MEDEX Northwest Division of Physician Assistant Studies, University of Washington, School of Medicine; Susan Storck, MD, FACOG, Chief, Eastside Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Group Health Cooperative of Puget Sound, Redmond, Washington; Clinical Teaching Faculty, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Washington School of Medicine. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
Notice: The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.