Duplex ultrasound
A duplex ultrasound is a test to see how blood moves through your arteries and veins.
See also:
How the Test is Performed
The test combines traditional ultrasound with Doppler ultrasonography. Regular ultrasound uses sound waves that bounce off blood vessels to create pictures. Doppler ultrasound records sound waves reflecting off moving objects, such as blood, to measure their speed and other aspects of how they flow.
There are different types of duplex ultrasound exams. Some include:
- Arterial and venous duplex ultrasound of the abdomen examines blood vessels and blood flow in the abdominal area.
- Carotid duplex ultrasound looks at the carotid artery in the neck.
- Duplex ultrasound of the extremities looks at the arms or legs.
- Renal duplex ultrasound examines the kidneys and their blood vessels.
The test is done in the ultrasound or radiology department.
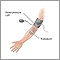
You may need to wear a medical gown. You will lie down on a table, and the ultrasound technician will spread a gel over the area being tested. The gel helps the sound waves get into your tissues.
A wand, called a transducer, is moved over the area being tested. This wand sends out the sound waves.
You need to stay still during the exam. You may be asked to lie in different body positions, or to take a deep breath and hold it.
A computer measures how the sound waves reflect back, and changes the sound waves into pictures. The Doppler creates a "swishing" sound, which is the sound of your blood moving through the arteries and veins.
Sometimes during a duplex ultrasound of the legs, the health care provider may calculate an ankle-brachial (ABI) index. You will need to wear blood pressure cuffs on your arms and legs for this test.
The ABI number is obtained by dividing the blood pressure in the ankle by the blood pressure in the arm. A value of 0.9 or greater is normal.
How to Prepare for the Test
Usually, there is no preparation for a duplex ultrasound.
If you are having an ultrasound of your stomach area, you may be asked not to eat or drink after midnight. Tell the person doing the ultrasound exam if you are taking any medicines, such as blood thinners, that might affect the results of the test.
How the Test Will Feel
You may feel some pressure as the wand is moved over the body, but there is usually no discomfort.
Why the Test is Performed
Duplex ultrasound is a less invasive option to arteriography and venography. A duplex ultrasound can show how blood flows to many parts of the body. It can also tell the width of a blood vessel and reveal any blockages.
A duplex ultrasound can help diagnose the following conditions:
- Abdominal aneurysm
- Arterial occlusion
- Blood clot
- Carotid occlusive disease (See: Carotid duplex)
- Renal vascular disease
- Varicose veins
- Venous insufficiency
A renal duplex ultrasound can also be used after transplant surgery to see how well a new kidney is working.
Normal Results
A normal result is normal blood flow through the veins and arteries. There is normal blood pressure and no sign of a narrowing or blockage of a blood vessel.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An abnormal result depends on the specific area being examined. An abnormal result may be due to a blood clot or plaque buildup in a blood vessel.
Risks
There are no risks.
Considerations
Cigarette smoking may change the results of an ultrasound of the arms and legs, because nicotine can cause the arteries to shrink (constrict).
Alternative Names
Vascular ultrasound; Peripheral vascular ultrasound
References
Marx J. Rosen’s Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 6th ed. St. Louis, Mo: Mosby; 2006.
Grainger RC, Allison D, Adam, Dixon AK. Diagnostic Radiology: A Textbook of Medical Imaging. 4th ed. Orlando, Fl: Churchill Livingstone; 2001.
Update Date: 5/23/2012
Reviewed by: David C. Dugdale, III., MD, Professor of Medicine, Division of General Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
Topics
Images
Read More
Patient Instructions
Notice: The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.