Chickenpox vaccine
The chickenpox vaccine protects against chickenpox, a disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus.
Information
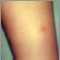
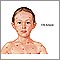
Chickenpox is caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). It is very common and spreads very easily. Chickenpox occurs more often in the winter and spring.
Most of the time, the infection is mild and not life-threatening. However, each year thousands of children or adults become seriously ill, need to be in the hospital, or even die from chickenpox.
The chickenpox vaccine works very well in preventing the disease. A small number of people who get the vaccine will still get chickenpox. However, they usually have a milder case than persons who did not receive the vaccine.
WHO SHOULD RECEIVE THIS VACCINE
Children should receive two doses of the traditional chickenpox vaccine.
- The first dose should be given when the child is 12 - 15 months old.
- A second dose should be given when they are 4 - 6 years old. This second dose can be given before age 4, as long as 3 months have passed since the first dose.
People 13 and older who have not received the vaccine and who have not had chickenpox should get two doses, 4 to 8 weeks apart.
People 13 and older who have had a previous dose and who have not had chickenpox should receive a second dose.
RISKS AND SIDE EFFECTS
The side effects from the chickenpox vaccine are generally minor and may include:
- Fever
- Mild rash
- Pain and swelling in the shot location
Only in very rare instances have more moderate or severe reactions been reported, including:
- Anaphylaxis (a severe allergic reaction; very rare)
- Pneumonia (very rare)
- Seizures (less than 1 out of 1,000 children)
Other reactions, such as low blood counts and brain involvement, are so rare that their link to the vaccine is questionable.
DELAY OR DO NOT GIVE THE VACCINE
The following people should not get the chickenpox vaccine:
- Pregnant women. Women who have received the vaccine should wait at least 1 month before getting pregnant. (Woman who are planning a pregnancy should be screened for immunity using a history or laboratory testing.)
- Children or adults who have a weakened immune system as a result of HIV/AIDS, cancer, organ transplants, or other factors
- Children who are taking aspirin or other salicylates
- Children or adults who are allergic to the antibiotic neomycin or gelatin
The following people should talk to their doctor about the proper timing of the chickenpox vaccine.
- Children or adults taking steroids for any condition
- Anyone who has recently received a blood transfusion or other blood product (including gamma globulin)
CALL YOUR PRIMARY HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IF:
- You are not sure whether the chickenpox vaccine should be given
- Any moderate to severe side effects appear after the injection
- Any alarming symptoms occur after the vaccine
- You have any other questions before or after receiving the vaccine
Alternative Names
Varicella zoster virus vaccine; Varivax; Vaccine - chickenpox
References
Chaves SS, Gargiullo P, Zhang JX, et al. Loss of vaccine-induced immunity to varicella over time. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1121-1129.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2012 Immunization Schedules for children 0 to 18 years of age. October 25, 2011.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommended immunization schedule United States. 2011 Proposed Revisions. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. October 28, 2010.
Conrod DV, Jack BW, Boggess KA. The clinical content of preconception care: immunizations as part of preconception care. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008 Dec;199(6 Suppl 2):S290-5.
Updated: 4/15/2012
Reviewed by: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
Notice: The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.