Gastroschisis repair - series
Aftercare
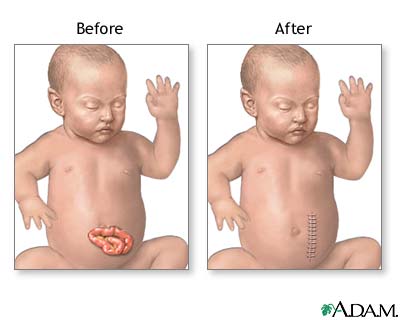
The defect can be corrected with surgery in most cases. The outcome depends on the amount of damage to or loss of intestine.
The infant is cared for post-operatively in a neonatal intensive care unit. The baby is placed in an isolette (incubator) to keep warm and prevent infection. The baby will be given oxygen and often require mechanical ventilation. Intravenous fluids and antibiotics and pain medication will be given. A nasogastric tube will be in place to keep the stomach emptied of gastric secretions. Feedings are started by nasogastric tube as soon as bowel function resumes. Feedings are started very slowly and often infants are reluctant to feed. These babies may need feeding therapy and lots of encouragement.
Update Date: 11/7/2011
Updated by: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
Related Pages
Notice: The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
