Growth hormone stimulation test - series
Normal anatomy
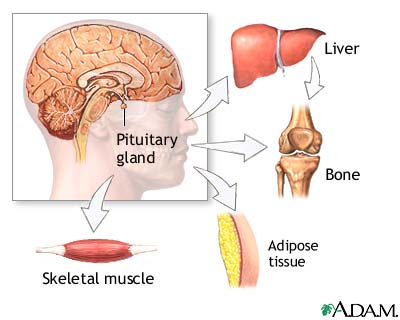
The growth hormone (GH) is a protein hormone released from the anterior pituitary gland under the control of the hypothalamus. In children, GH has growth-promoting effects on the body. It stimulates the secretion of somatomedins from the liver, which are a family of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) hormones. These, along with GH and thyroid hormone, stimulate linear skeletal growth in children. In adults, GH stimulates protein synthesis in muscle and the release of fatty acids from adipose tissue (anabolic effects). It inhibits uptake of glucose by muscle while stimulating uptake of amino acids. The amino acids are used in the synthesis of proteins, and the muscle shifts to using fatty acids as a source of energy. GH secretion occurs in a pulsatile (short, concentrated secretion) and sporadic manner. Thus, a single test of the GH level is usually not performed.
Update Date: 4/20/2010
Updated by: Ari S. Eckman, MD, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
Notice: The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
