White blood cell count - series
Results
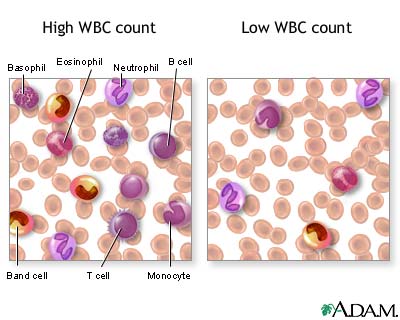
Interfering factors: Acute emotional or physical stress can increase WBC counts. There are various types of white blood cells (WBCs) that normally appear in the blood: neutrophils (polymorphonuclear leukocytes; PMNs), band cells (slightly immature neutrophils), T-type lymphocytes (T cells), B-type lymphocytes (B cells), monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. T and B-type lymphocytes are indistinguishable from each other in a normal slide preparation. Any infection or acute stress will result in an increased production of WBCs. This usually entails increased numbers of cells and an increase in the percentage of immature cells (mainly band zcells) in the blood. This change is referred to as a "shift to the left" People who have had a splenectomy have a persistent mild elevation of WBCs. Drugs that may increase WBC counts include epinephrine, allopurinol, aspirin, chloroform, heparin, quinine, corticosteroids, and triamterene. Drugs that may decrease WBC counts include antibiotics, anticonvulsants, antihistamine, antithyroid drugs, arsenicals, barbiturates, chemotherapeutic agents, diuretics and sulfonamides. Normal values: WBC: 4,500 to 10,000 cells/mcl Note: cells/mcl = cells per microliter What abnormal results mean: Low numbers of WBCs (leukopenia) may indicate: bone marrow failure (for example, due to granuloma, tumor, fibrosis) presence of cytotoxic substance collagen-vascular diseases (such as lupus erythematosus) disease of the liver or spleen radiation High numbers of WBCs (leukocytosis) may indicate: infectious diseases inflammatory disease (such as rheumatoid arthritis or allergy) leukemia severe emotional or physical stress tissue damage (for example, burns)
Update Date: 2/13/2011
Updated by: David C. Dugdale, III, MD, Professor of Medicine, Division of General Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
Notice: The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
