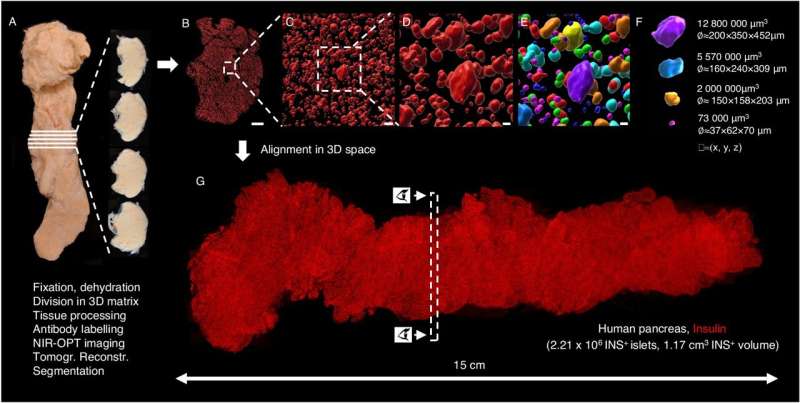
Researchers at Umeå University have succeeded in imaging an entire human organ, a pancreas, in microscopic resolution. By staining different cell-types with antibodies and then using optical 3D imaging techniques to study the entire organ, their data provides a partially new picture of the pancreas.
The results may be of great importance for diabetes research, especially when developing various new forms of treatment. The study is published in Nature Communications.
The pancreas is a key organ for the development of diabetes, a disease that today affects over half a billion people. It contains millions of small cell clusters, the so-called islets of Langerhans, which function to regulate blood sugar levels in the body.
The islets chiefly contain beta- and alpha-cells that produce the hormones insulin and glucagon, respectively. Insulin is secreted into the bloodstream and acts much like a key to unlock the body’s cells so that they can take up sugar (glucose) after a meal, the main form of energy used by the body. Glucagon in turn releases glucose stores when we need a supply of energy. These two cell-types also communicate directly with each other to optimize the correct glucose level in the body.
“Both insulin and glucagon cells were discovered over a hundred years ago, and it has long been believed that the islets should contain both cell types to form a fully functioning unit,” says Ulf Ahlgren, professor at the Department of Medical and Translational Biology.
Since the islets of Langerhans make up only a small percentage of the pancreas, even though they occur in such large numbers, they have historically been very difficult to study directly within the pancreas. In most cases, researchers have had to study tissue sections that only provide a 2D image of a very small part of the organ. Now, Umeå researchers have used optical 3D techniques in which different cell-types can be marked with fluorescently colored antibodies.
Entire organ at microscopic resolution
“By dividing the entire organ into smaller parts, we enable the antibodies to get where they need to go. Since we know where each piece comes from, we can then, after scanning the different parts individually, ‘reassemble’ the entire pancreas again using computer software. This allows us to perform a plethora of calculations and study which cell-types are present, as well as where they are located in 3D space, as we know the 3D coordinates, their volume, shape and other parameters for each and every stained object in the entire organ,” says Ahlgren.
In addition to new data on how insulin-producing cells are distributed in the pancreas, the researchers now show that glucagon-producing cells are not present in as many as 50% of the islets of Langerhans that do contain insulin cells. This is contrary to what was previously thought, where islets were believed to contain both insulin- and glucagon-expressing cell-types with the same islet.
“This was a surprise to us, and I believe that these results may be of great importance for diabetes research. First, it shows that the islets have a much more uneven composition, or cellularity, than previously thought. This could mean that islets of different composition might be specifically specialized to respond to different signals and/or operate in different metabolic environments. Of course, we really want to find this out,” says Ahlgren.
“Second, a great deal of research in the diabetes field is carried out on isolated islets of Langerhans from deceased donors. Since we also show that this uneven composition is largely linked to islet size, it means that results from such experiments may not fully reflect how the islets are structured and function in the living pancreas. This could potentially be important for everything from islet transplants in type 1 diabetes to studies trying to produce islets of Langerhans from stem cells.”
Basis for future studies
The research team will now continue to work to see if their methods can be used to determine whether other cell types in the pancreas also contribute to the formation of the islets in a way that has not previously been known. In addition, they will study whether it looks similar in mouse models, which could affect the use of mice for preclinical diabetes research.
“The methods and data we are now publishing will be able to form an important basis for future studies of human material in order to better understand what happens in the pancreas in the development of type 1 and type 2 diabetes, but also for diseases such as pancreatic cancer,” says Ahlgren.
More information:
Joakim Lehrstrand et al, Illuminating the complete ß-cell mass of the human pancreas- signifying a new view on the islets of Langerhans, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-47686-7
Citation:
New findings on pancreatic anatomy may affect diabetes research and treatment (2024, April 22)
pancreatic-anatomy-affect-diabetes-treatment.html
.
. The content is provided for information purposes only.
